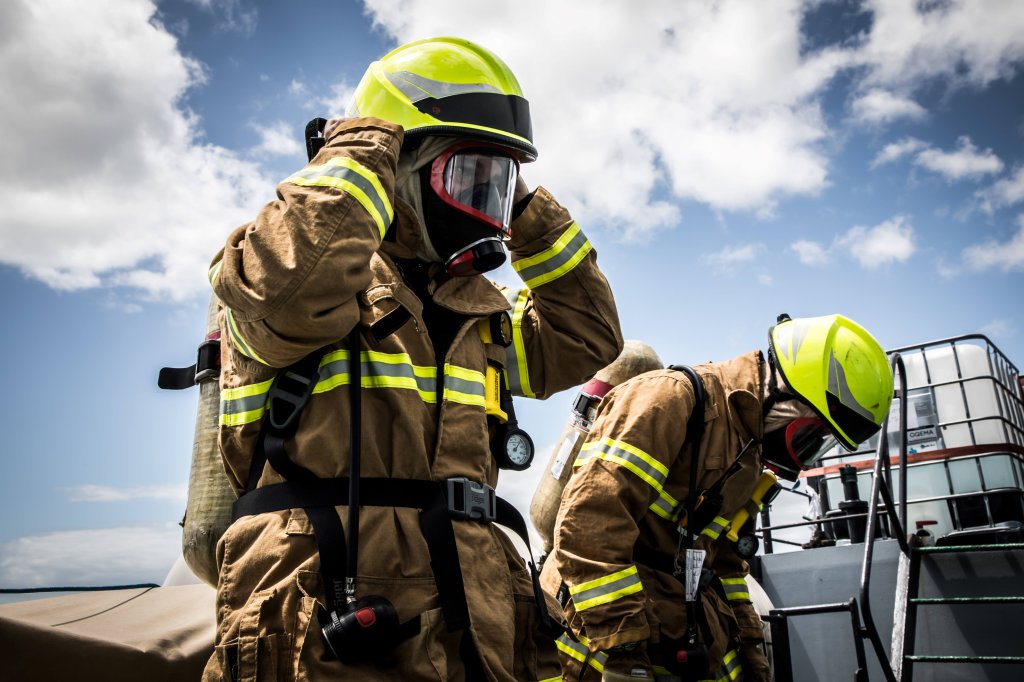
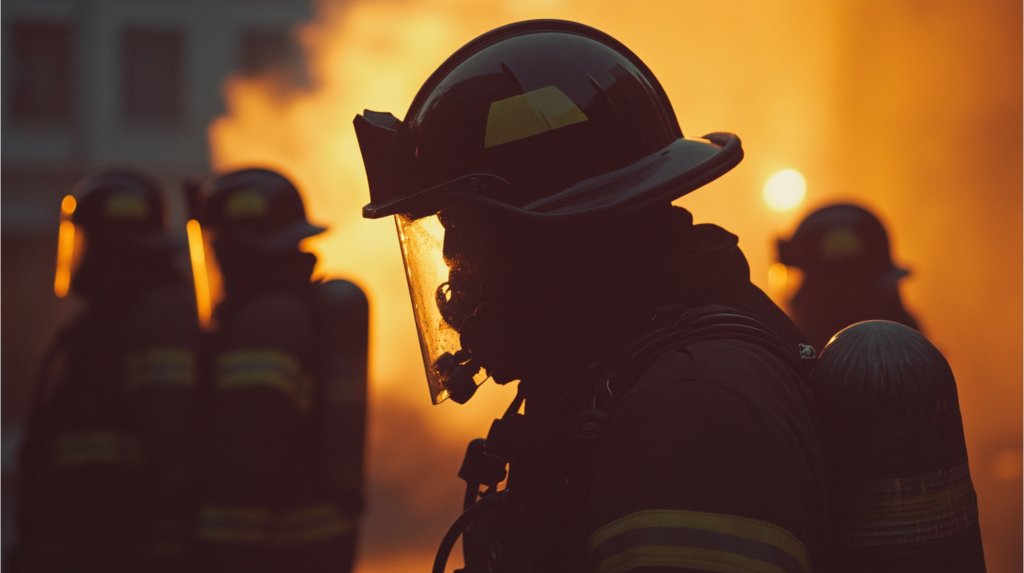
Firefighter gear is essential to the safety and performance of firefighters as they respond to emergency situations. The materials used in firefighter gear must withstand intense heat and flames while protecting them from hazardous fumes and debris. This means that it is important for departments to choose the right plastic when replacing or upgrading their firefighter gear.
Plastics have a range of physical properties that help protect firefighters during increasingly intense situations. Below, you'll learn more about how firefighters use plastic during day-to-day operations.
An Expert is just around the corner.
With over 100 years of combined product knowledge and industry experience, we are confident our plastics experts can help you find a solution for your application.
What Are the Most Fire-Resistant Plastics?
The fire-resistant plastics firefighters use all fall under the fluoropolymer (PFAS) category. They are also known as thermopolymers or thermosets, which include a wide range of plastics with heat and chemical resistance.
The following temperatures may vary depending on the material’s enhancements.
Polyetherimide (PEI) is heat resistant (up to approximately 219°C) and has excellent mechanical strength. PEI has low smoke emission rates and a high melting point, making it ideal for firefighting operations. It also offers good chemical resistance properties and beats most environmental hazards.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), or Teflon® (a registered trademark of DuPont), is a soft plastic known for heat (up to about 316°C when used intermittently) and chemical resistance. It's best known for being used in non-stick cookware but has a high melting point and doesn't react with most things, making it one potential option as a moisture barrier.
Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) is a heat-resistant thermoplastic surviving temperatures up to approximately 250°C when used continuously. It's used as a replacement for metal, making it ideal for heavy-duty firefighter applications. It was introduced alongside PBI as an injection moldable blend named Celazole T-Series.
Polybenzimdazole (PBI) has the highest heat resistance (in excess of 500°C), making it ideal for the riskiest situations. The fibers of PBI have no known melting point and do not burn. Due to the expenses behind its manufacturing, it's reserved for the most dangerous applications.
Melamine is a unique compound that releases nitrogen gas when burned. Basofil®, a fire-retardant fiber, is one application of fire-retardant material. It's also used to manufacture heat-resistant plastic cookware and kitchen tiles.
These plastics can be found in many forms of firefighter equipment. Below, you'll learn more about those specific applications.
Which Plastic is Used in Firefighter's Uniforms
One of the most common plastics you'll find in firefighters' uniforms is melamine. This material is often used to coat the uniform, adding an extra layer of protection for those in the line of duty.
The coating is fire-resistant, so you might find it across fire-resistant fabrics, including mattresses. You also might find it used in transportation (like buses or airplanes) to prevent the spread of fire.
The material under the coating is often Kevlar® (a registered trademark of DuPont), which acts as a moisture barrier. Kevlar® is a manufactured plastic that's lightweight and durable, allowing firefighters to remain mobile.
What Plastic is Used in Firefighter's Helmets?
Firefighters' helmets are made from different plastics and fabrics, including polycarbonate, which are all designed to be heat resistant. Below is a quick list of various plastics you might find:
Polycarbonate: Many built-in eye and face shields are made from a clear and strong material called polycarbonate. It is a popular option for helmet manufacturers because polycarbonate provides excellent impact protection and high temperature resistance.
Aramid(aromatic polyamide): A class of fibers known for their heat resistance. Kevlar® is the most well-known brand of Aramid, which is popular for use in aerospace and military applications.
Polysulfone (PSU): A group of thermoplastics known for their strength against high temperatures. Because this material is see-through, you'll often find it on helmet visors and face shields. It’s not as impact resistant as polycarbonate, but it has 3 times the thermal performance.
Polyamide: The synthetic form of polyamide is used across transportation for its natural durability and thermal resistance. Natural forms include wool, which is not often used in helmets.
Polyurethane (PU): This class of thermoplastic polymers includes a wide range of potential options. The type of polyurethane most used in helmets is thermoplastic, which consists of some items in the list above.
Firefighter helmets have seen numerous upgrades from the classic caps, typically made of Bakelite. This fire-resistant plastic was discontinued as time passed, meaning you'll most likely find this plastic in antique shops. However, the continuous need to upgrade firefighting technology ultimately stems from the priority of protecting our firefighters in the field.
Are Wildfires Getting Worse?
We are seeing more burned acreage, according to data from various sources. This situation applies to the entirety of North America.
California is one such example, seeing an increased number of more severe fires across the state. This has risen steadily since the 1980s. However, recent years have seen a greater impact with dry conditions.
Canada has also seen a record 25 million scorched acres since the beginning of 2023 (based on data from the middle of July). This is up from the late 80s when Canada experienced the loss of over 18 million acres. Knowing that peak fire season has yet to pass based on this data, this number is expected to climb.
High temperatures and a major heat wave have spurred these fires, creating dry conditions. Therefore, it’s our responsibility to be careful to prevent actions that could potentially start a fire.
This is why we are seeing improvements in firefighter equipment quality and heat resistance. You even see these changes taking place in vehicles.
Why Firetrucks are Going Plastic
Not only do thermoplastics have the potential to withstand major temperatures, but they also have additional benefits. Below is a list of reasons firetrucks are going plastic:
- Thermoplastics are becoming more heat-resistant each year, making them more appropriate for building materials and vehicle applications.
- Plastic is naturally corrosion-resistant, while metal is more likely to get eaten away from water.
- Plastic can be inexpensive compared to metal costs, especially when replacing water tanks.
- Modern plastics are much more long-lasting than some might assume, so they are used more often across automotive applications.
- Firetrucks are heavy vehicles, so reducing their weight can help firefighters maintain control at high speeds.
Regarding specialty vehicles, plastic is more adaptable and long-lasting than metal. As we continue to develop stronger, heat-resistant plastics, you can expect them to find more applications.
How the Right Plastics Enhance Safety and Performance
Firefighters have a tough job, and we must ensure their safety at all costs. Choosing the right plastic for firefighter gear is essential to enhance firefighters’ safety and performance.
Aramid, polysulfone, polyamide, and polyurethane are some of the most commonly used plastics in firefighter gear due to their heat resistance and strength. As wildfires become more severe, these plastics are becoming increasingly valuable and will continue to be used in the future.
Need More Information?
To find out how plastic can help improve your operations’ safety, contact our Piedmont Plastics team!
Discover More

