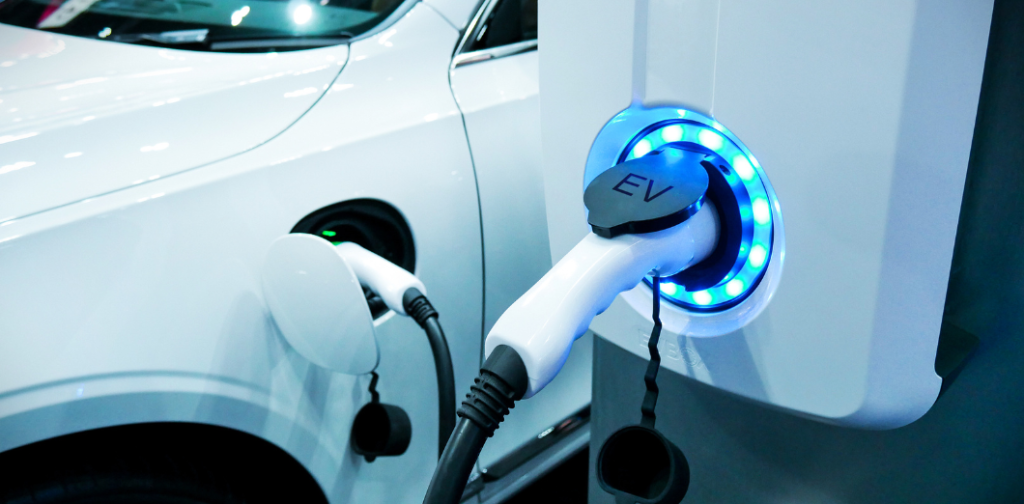
Lightweight Materials for Electric Vehicles
The shift from combustion engines to electric powertrains has introduced more than new propulsion methods; it has significantly changed the way vehicles are engineered. Electric vehicles (EVs) require materials that not only perform under extreme electrical and thermal loads but also contribute to range, reliability, and regulatory compliance.
While metals still play a significant role, performance plastics are emerging as the leading choice in areas where weight savings, safety, and design flexibility are of utmost importance.
An Expert is just around the corner.
With over 100 years of combined product knowledge and industry experience, we are confident our plastics experts can help you find a solution for your application.
Engineering Lightweight Efficiency
When your EV is already carrying a battery that can weigh half a ton, every ounce saved elsewhere really counts. That’s why smart engineers are turning to performance plastics to trim weight without compromising strength, durability, or safety.
These materials deliver the muscle to support structural loads, minus the metal bulk, making them a perfect fit for today’s lightweight design strategies.
Here’s where plastics are making a big impact:
Glass-reinforced nylon for strong, lightweight brackets and support frames
Acetal (POM) for rigid, low-friction components like clips, bushings, and gear parts
Polypropylene for durable, chemically resistant trays and underbody panels
ABS for molded parts that combine toughness with sleek, integrated features
Materials That Manage Heat and Voltage
EV systems operate under higher temperatures and voltages than traditional vehicles. Battery packs and inverters generate significant heat, and any material surrounding high-voltage components must be electrically insulating, flame-retardant, and dimensionally stable.
Materials such as flame-rated polycarbonate, PC/ABS blends, and glass-filled PBT meet the UL 94 V-0 standards while keeping structural integrity up to ~125°C or higher.
In battery modules, these plastics serve as cell separators, covers, and tray enclosures, preventing arc flash and minimizing fire propagation, while allowing for precision-molded part integration, such as vent paths or sensor mounts. Some formulations also include thermally conductive fillers, allowing for effective heat dissipation without compromising insulation.
Chemical Resistance and Mechanical Longevity
Electric vehicles run in harsh environments, including salt spray, road grime, engine heat, and cooling fluids, all of which are constantly in motion. That’s why the materials you choose for mechanical parts can’t just be strong; they need to withstand chemical exposure and years of wear. Fortunately, engineering-grade plastics are designed to withstand it all.
Standout performers include:
- Acetal (POM) for bushings, gears, and impellers where low friction and tight tolerances are critical
- Polypropylene for under-hood and fluid-facing parts that shrug off chemicals, moisture, and thermal cycling
Integration and Manufacturing Efficiency
Injection-molded plastics enable complex geometries that combine structure, sealing, and fastener features into a single piece, eliminating the need for assemblies and reducing part count.
This capability is critical in EVs, where battery trays, connector housings, and enclosure systems benefit from integrated cooling channels, EMI shielding barriers, and wire guides.
Some designs replace 3–5 metal brackets or stamped parts with a single glass-filled polymer component, reducing labor and tolerance issues while lowering mass.
Plastic Applications Across the EV Industry
Plastics aren’t just filling gaps in EV design; they’re driving real innovation across nearly every system in the vehicle. From battery enclosures to cooling lines and electrical connectors, advanced polymers are doing the heavy lifting where strength, safety, and precision all matter. These materials are lighter than metal, easier to mold into complex shapes, and built to handle the harshest operating conditions without missing a beat.
Here’s how plastics are transforming key EV systems:
Battery enclosures made from flame-rated PC/ABS or nylon provide structural strength, electrical insulation, and integrated features like EMI shielding or venting
Cooling system parts such as pump housings and manifolds rely on acetal and glass-filled polypropylene for their chemical resistance and thermal stability
Power electronics housings use UL 94 V-0 thermoplastics to protect inverters and converters from heat and electrical faults
High-voltage connectors and busbar mounts are often built from nylon 6/6 or PBT for their tracking resistance and precision fit
The Road Ahead
EV adoption continues to accelerate, and so does the need for materials that support performance, reliability, and compliance. Piedmont Plastics supports EV manufacturers and suppliers with a broad portfolio of UL-certified, automotive-grade polymers available in sheet, rod, or machined forms. Our specialists can assist with material selection, specification support, and supply logistics for high-volume production or custom prototyping.
If you're building the next generation of electric vehicles, contact Piedmont Plastics. We’ll help you source the flame-resistant, impact-tough, and weight-saving plastics that make high-voltage mobility a reality.
Achieve More Mileage With Performance Plastics
Looking for more information on how our lightweight plastics can propel your electric vehicle project forward? Connect with our team of experts today!
Get In Touch

