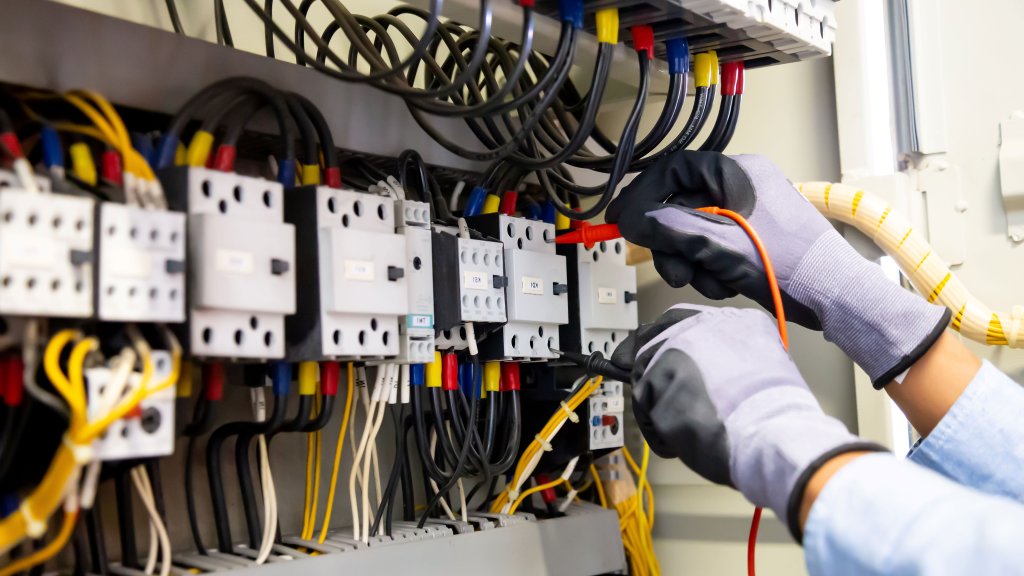
Safe Circuits
Plastics play a crucial role in securing our electrical systems. These versatile materials, from insulation to safety, have become essential in various electronic applications.
In this article, we will explore the top plastics that are driving our electrical world forward. But first, let's talk about how plastics support today's electronics.
An Expert is just around the corner.
With over 100 years of combined product knowledge and industry experience, we are confident our plastics experts can help you find a solution for your application.
Five Reasons Electronics Rely on Plastics
1. Heat Response and Stability: Understanding Plastics' Thermal Behavior
Plastics possess unique thermal properties that determine their behavior when exposed to heat. One such property is their heat response, which refers to how plastics react when subjected to high temperatures.
Unlike many other materials, plastics have a relatively low melting point, which allows them to be easily molded into various shapes and forms. However, this property also means some plastics can deform or lose structural integrity if subjected to excessive heat.
To combat this issue, we carefully select plastics used in electrical applications for their high resistance to thermal degradation. Thermal degradation occurs when a material breaks down or deteriorates because of exposure to heat.
2. Insulating Power of Plastics: Preventing Electrical Hazards
Electrical insulation involves insulating materials to prevent electrical conductivity and protect against short circuits and electrical shocks. For example, plastic electrical enclosers must protect against shocks when a user touches them.
Plastics have high resistivity, meaning they do not readily conduct electricity. This prevents unwanted electrical currents from flowing through electrical components, reducing the risk of short circuits and electrical hazards.
3. Flame Resistance: Plastics in Fire Prevention
Electrical fires pose a significant risk to both property and human lives. These fires can result from various factors, such as faulty electrical wiring, overloaded circuits, or electrical equipment malfunctions. Flame-retardant plastics can help prevent these disasters.
For example, wires in electrical applications rely on a plastic coating. Thing protects the weaker electrical wires underneath and is made of a flame- and heat-resistant material.
In addition, high-performance plastics can handle heavy-duty work at refineries. So, if you can find it in the oil and gas industry, there's bound to be some use in the electrical industry.
4. Chemical and Moisture Immunity: Plastics' Protective Qualities
Exposure to solvents and moisture can be highly detrimental to electrical equipment and components. Chemicals and liquids can corrode metal components, disrupt electrical conductivity, and cause short circuits or equipment failure. Moisture, another risk, can lead to the formation of condensation, increasing the risk of insulation breakdown and electrical discharges.
Plastics offer an effective solution to these challenges. By nature, plastics are inherently resistant to solvents and moisture because of their molecular structure. This resistance is further enhanced through the use of additives and special formulations specifically designed for electrical applications. You can check out our product reference chart for more information on what plastics include additives.
Plastics' moisture resistance is equally notable. Unlike materials like wood or paper that can absorb and keep moisture, plastics are inherently hydrophobic, meaning they repel water. That's why you can find plastics in watercraft manufacturing, protecting the electrical components inside of boats.
5. Robustness and Resilience: The Mechanical Strength of Plastics in Electrical Use
Durability is a key aspect of using plastics in electrical contexts. Electrical components are often exposed to harsh conditions, including vibrations, impacts, and fluctuations in temperature. Therefore, you see plastic in heavy-duty applications, like heavy equipment.
Plastics also can resist deformation and maintain their structural integrity, which is vital under load-bearing conditions. Electrical components often need to bear mechanical forces and strains without breaking or collapsing. Plastics provide the required strength to support these loads without compromising the electrical system's performance. Some plastics can also withstand vibrations and effects, preventing damage to fragile internal parts.
Top 8 Plastic Materials for Electrical Use
Plastics play a crucial role in the electrical industry, providing many benefits and applications. From insulating materials to protective casings, here is a brief overview of some of the top plastics commonly used in the electrical field.
1. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is one of the most widely used thermoplastics in the electrical industry. Its excellent electrical insulation properties make it ideal for insulation on wires and cables, helping to prevent electrical leakage and ensure safe and efficient power transmission. PVC is also known for its durability and resistance to moisture, chemicals, and weather, making it a reliable choice for outdoor electrical applications.
CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride) is a unique variant at Piedmont Plastics. It includes a chlorination process, making CPVC ideal for industrial operations.
2. Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is a highly durable and versatile thermoplastic used in various electrical applications. Its high strength-to-weight ratio is ideal for structural components like connectors, terminals, and housings.
You can also get medical-grade, making it ideal for both electrical and sterile environments.
3. Polyethylene
Polyethylene (PE) is another popular plastic used in electrical systems. Its high dielectric strength and excellent insulation properties make it suitable for cable and wire insulation and insulating bushings and transformer components. PE also offers good resistance to electrical arcing and corona discharge, reducing the risk of electrical breakdowns and ensuring the longevity of electrical components.
HDPE, or high-density polyethylene, is a unique variant you can get at Piedmont Plastics. This variant is ideal for everything from manufacturing to food safety (as well as electronics)
4. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
ABS is a three-part thermoplastic polymer that can be used for various electrical applications. Its impact resistance and mechanical strength make it suitable for electrical enclosures, housings, and connectors. ABS also offers good chemical and flame resistance, making it ideal for hazardous locations.
5. Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is known for its high melting point, chemical resistance, and low moisture absorption. These properties make it suitable for various electrical applications, including capacitors, battery casings, and switches. PP's excellent electrical insulation properties and dimensional stability make it a reliable choice in electrical systems subjected to high temperatures and harsh environments.
6. Phenolic
Phenolic is an industrial laminate created using a resin system. You can commonly find them to reinforce existing items, such as electronics. Its strong bond strength and excellent insulation properties are ideal for connectors, switches, and other electrical components exposed to high temperatures.
7. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon® (a registered trademark of DuPont), is widely used in electrical applications because of its exceptional electrical insulation properties and high thermal stability.
PTFE is resistant to heat, moisture, and chemicals, making it ideal for electrical connectors, sockets, and high-temperature wiring applications. Its low friction coefficient and non-stick properties also contribute to the efficiency and reliability of electrical systems.
8. Polyamide (PA)
Polyamide (PA), known as nylon, is known for its excellent mechanical strength and heat resistance. It is commonly used as an insulating material for electrical connectors, switches, and circuit breakers because of its resistance to high temperatures and the ability to withstand mechanical stress. PA's ability to maintain its shape and strength in demanding conditions contributes to the safety and performance of electrical components.
What Plastic is Best for My Application?
Despite these amazing electronic applications, you might still wonder what plastic fits your electronic needs. To truly find out, send us a message about your situation. From there, you can get the advice you need to find the right plastic for your application.
Contact Us Today!
