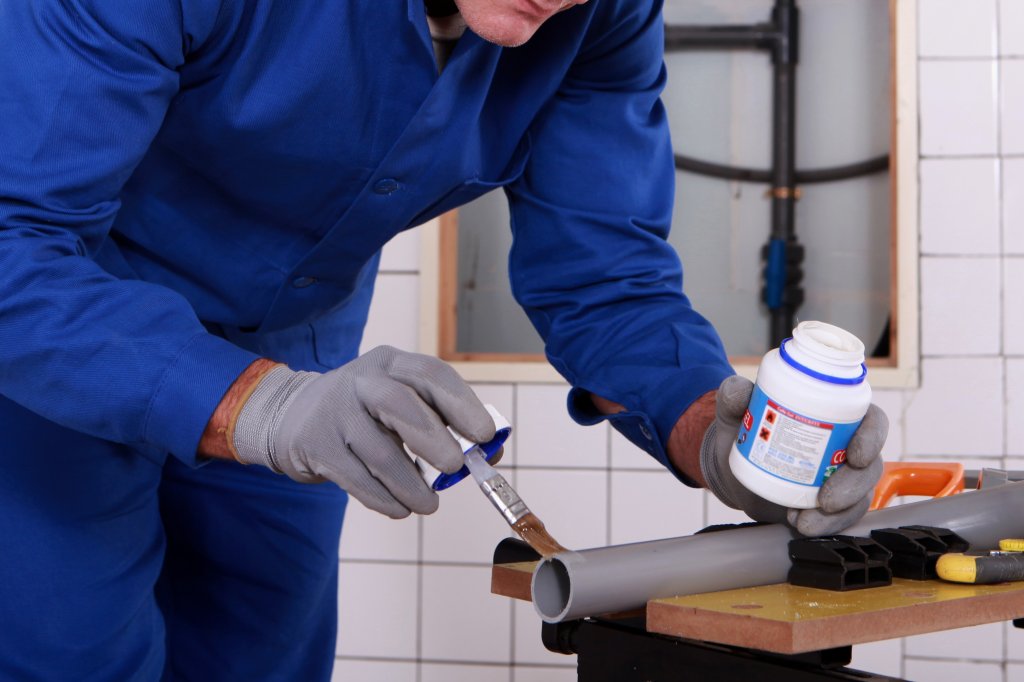
Stronger and More Durable Bonds
Bonding plastics is essential in manufacturing and product assembly, from the water bottle you drink to car interior components. Understanding the art and science of bonding plastics is crucial for creating durable and reliable end products.
Plastic bonding involves joining plastic components using various techniques such as solvent, ultrasonic, and adhesive. These methods play a crucial role in ensuring the strength and integrity of the final product. Moreover, different types of plastics require specific bonding techniques to achieve optimal results, making it essential to understand the best practices for bonding popular plastics like PVC, ABS, and polycarbonate.
This article will investigate the key bonding techniques for plastics, explore how different bonding methods impact product performance, and discuss the latest advances in plastic bonding. Additionally, we will provide valuable insights into solving common bonding issues, equipping you with the knowledge to enhance the quality and durability of plastic-bonded products.
Key Bonding Techniques
Bonding plastics is an art and science vital in many industries. Here's a clear overview of the prominent techniques:
Solvent Bonding
Ideal for PVC and acrylics
It uses a solvent to dissolve the surfaces partially. As the solvent evaporates, a formidable bond is formed. Its precision makes it popular where the physical properties of the plastics are compatible with solvents.
Ultrasonic Bonding
Applied to thermoplastics like ABS
Ultrasonic bonding (also known as ultrasonic welding) generates frictional heat via high-frequency vibrations to meld plastic substrates, ensuring a clean bond with high tensile strength.
Adhesive Bonding
A versatile method suited for various plastic materials
It employs specialized adhesives (such as epoxy matrices or rubber-like materials) tailored to the substrates' surface energy and thermal conductivity. Adhesive formulations range from epoxies to cyanoacrylates, offering robust solutions regardless of environmental conditions.
Crucial to each method is surface preparation. Effective bonding demands substrates with good surface wettability, which may require treatments like cleaning or abrasion. Hybrid techniques might combine these methods for complex, mixed-adhesive joints, often seen in composite substrates within industries focused on advanced materials.
| Bonding Method | Material Suitability | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Solvent | PVC, Acrylics | Surface Energy |
| Ultrasonic | ABS, Polycarbonate | Tensile Strength |
| Adhesive | Wide range | Environmental Conditions |
Bonding Methods for Popular Plastics
Bonding popular plastics such as PVC, ABS, and polycarbonate involves overcoming challenges like poor surface wettability and chemical inertness. A remarkable solution is cold gas plasma modification, which enhances adhesion by chemically activating the surface for better bond formation. Thorough cleaning, surface roughening, and applying primers are essential surface preparations that promote mechanical interlocking—key to reliable adhesive bonding.
Hybrid bonding techniques stand out by merging different adhesives or combining adhesive application with heat and pressure, fostering stronger connections, especially for dissimilar materials. Moreover, plasma, corona treatments, or laser ablation play a pivotal role in modifying surface properties, thus improving bond compatibility.
Selecting an ideal adhesive is critical; it should display high bond strength, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors to ensure a formidable bond with these plastics. Below are concise recommendations for effective bonding of PVC, ABS, and polycarbonate:
| Plastic Type | Surface Modification | Adhesive Type |
|---|---|---|
| PVC | Plasma/Corona treatment | High-strength epoxy |
| ABS | Plasma/Laser ablation | Flexible cyanoacrylate |
| Polycarbonate | Priming/Roughening | UV-curable adhesive |
Resolution of surface challenges and systematic selection of adhesives contribute significantly to achieving durable and robust bonds with these widely-used materials.
Improving Product Performance
Precise bonding methods are paramount for optimizing a product's strength and appearance. Proper surface preparation, such as cleaning and roughening, prepares substrates for better adhesion—critical for an aesthetically pleasing and durable end product.
Hybrid bonding techniques adeptly address the complex needs of joining dissimilar materials, directly influencing the structural integrity and finish of the composite substrates. These innovative methods, which may combine varying adhesive formulations, are tailored to the physical properties of the materials to ensure a seamless and robust bond.
Advanced surface modification techniques, including plasma and corona treatments, play a catalytic role in enhancing surface energy, thus promoting adhesion. This not only fortifies the bond but also substantially boosts surface appearance.
The strategic use of intermediary layers acts as a connective tissue, smoothing out the disparities between polymeric substrates, which otherwise impede strong adhesion—this translates into a more cohesive look and fortified composition of the final product.
On the thermal front, managing expansion disparities through adhesives with sound thermal conductivity or flexible designs is crucial. It preserves the structural and aesthetic attributes against thermal stresses, maintaining product performance across various environmental conditions.
| Bonding Approach | Outcome on Strength | Influence on Appearance |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Prep | Enhanced adhesion | Improved smoothness |
| Hybrid Technique | Increased integrity | Seamless finish |
| Surface Modify | Stronger bonds | Enhanced compatibility |
| Intermediary Layer | Compatibility boost | Cohesive look |
| Thermal Management | Stability maint. | Consistent appearance |
Effective bonding elevates the mechanical performance and visual appeal, which are vital for the success of products in sectors like the automotive industry and beyond.
Plastic Bonding Technology Booming
Innovative bonding technologies are revolutionizing the plastics industry, with reactive composition systems at the forefront. Utilizing components like methylene malonate and beta ketoesters, modern adhesives create interpenetrating polymer welds, pushing the boundaries of adhesion properties and strength.
The rampant global counterfeiting issue, exceeding $1.7 trillion, compels the integration of security features into bonding processes. Advanced plastic bonding techniques offer overt and covert authentication solutions to protect product integrity.
Adhesive choices have expanded to include robust options such as epoxy, polyurethane, and cyanoacrylate, each with unique benefits catering to high bond strength, flexibility, and environmental resistance. This diversity reflects the maturation and adaptability of bonding materials to meet varied needs.
Surface modification technology has also seen a surge. Plasma, corona treatments, and laser ablation are pivotal in altering plastic surfaces and enhancing bonds and compatibility with mixed materials.
| Surface Treatment | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Plasma Treatment | Increased surface energy |
| Corona Treatment | Enhanced adhesive wettability |
| Laser Ablation | Precision surface modification |
Finally, thermal management has gained traction. Adhesives showcasing excellent thermal conductivity and flexible joint designs are seminal in responding to thermal stresses—highlighting a key trend in the evolution of plastic bonding methods.
Solving Common Bonding Issues
Bonding polymeric and rubber-like materials can be difficult due to their low surface energy and hydrophobicity. To surmount these obstacles, Low-Pressure Cold Gas Plasma treatment is essential for enhancing surface wettability and ensuring a strong adhesive bond.
Selecting the right adhesive is another critical step in the bonding process. Options cover a wide range, from epoxy to polyurethane and cyanoacrylate adhesives, each chosen for its specific physical properties – whether it's tensile strength, flexibility, or resilience under varying environmental conditions.
Surface preparation must not be overlooked. A thorough clean, sometimes augmented by a roughening process or the application of a primer, can significantly improve mechanical interlocking and broaden the surface area for stronger adhesion.
| Surface Prep Techniques | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Cleaning | Removes contaminants |
| Roughening | Increases mechanical interlock |
| Priming | Enhances bonding surface area |
Where direct bonding proves insufficient, intermediary layers can be the bridge between disparate materials, fostering compatibility and reinforcing the bond. Hybrid bonding strategies, which may meld diverse adhesives or integrate heat and pressure applications, offer tailored solutions to enhance bond durability and performance in even the most demanding applications.
Need Help?
Choosing the right adhesive, based on specific physical properties, is crucial. Surface preparation techniques, such as cleaning, roughening, and priming, can significantly improve mechanical interlocking and adhesion.
Intermediary layers and hybrid bonding strategies provide tailored solutions to enhance bond durability and performance when direct bonding falls short.
Whether you work in manufacturing or product development, understanding these techniques and staying updated with the latest advances can create stronger, more reliable, and aesthetically pleasing plastic-bonded products. If you have any questions or need further information, don't hesitate to contact our team of experts for guidance and assistance in your bonding projects.
An Expert is just around the corner.
With over 100 years of combined product knowledge and industry experience, we are confident our plastics experts can help you find a solution for your application.
